ControlAltDieliet 

- Home /
- Mattermost /
- Introduction to Integrations /
- Outgoing Webhooks
Sending (and receiving) data
with an outgoing webhook
In the previous article you learned how to receive data from an external source.
Now you learn how to send a request or data to an external source. We use Outgoing Webhooks for this.
Outgoing Webhooks are the easiest way to send a request or data to another program from a public channel
We already receive alerts in Mattermost when the temperature of a fridge is too high. But what if we want to check the current temperature? We want to send a request to our fridges to give us the actual temperatures.
Has everything returned to normal, we don't need to go to the fridges and check them.
Outgoing webhooks are only available in public channels and you can't send any variables with them. If you want to send variables or send and receive data in private channels or group messages, you need to use slash commands.
We handle slash commands in Part III of this tutorial!
1 Create the Outgoing Webhook in four steps
1 Go to the Menu and choose Integrations
2 In the following screen, choose Outgoing Webhooks.
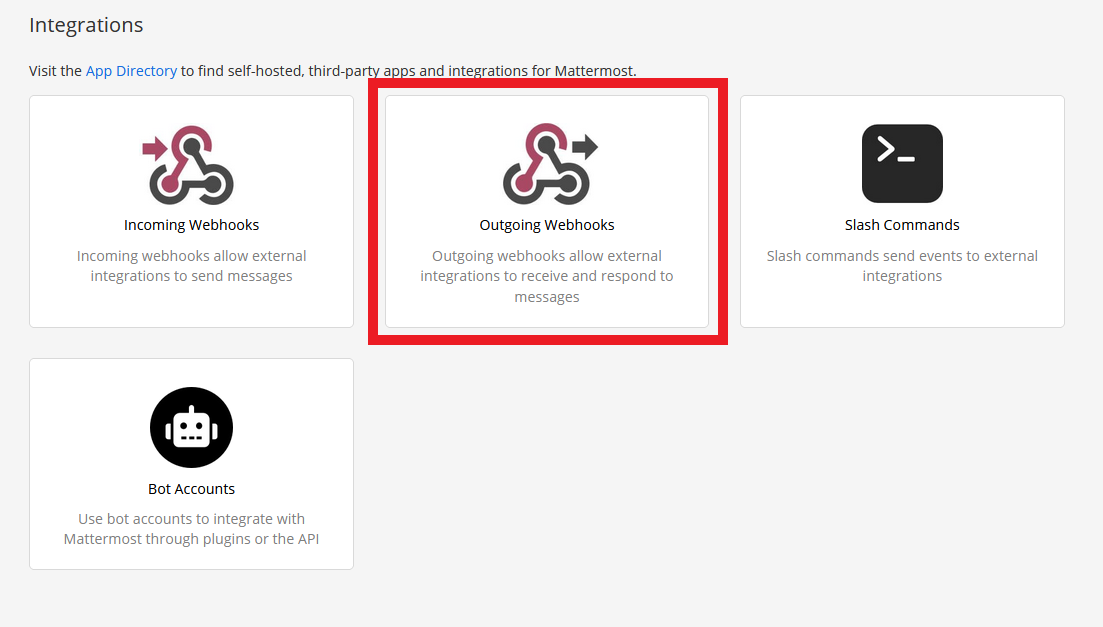
3 In the following screen, you see your existing Outgoing Webhooks and you can add a new one.
4 Now we setup the Outgoing Webhook in the next screen.
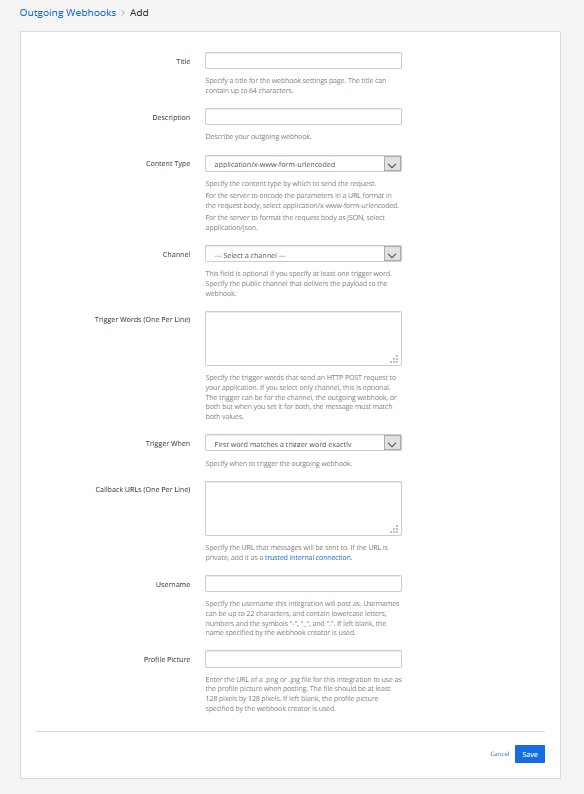
- Give the outgoing webhook a title
- Give the outgoing webhook a description
- Specify the Content Type of the request you will receive : www-form-urlencode or JSON
- Select a channel or specify the trigger words to send an HTTP POST request to the webhook (Trigger words only work in public channels. For using your outgoing webhook in a private messages you need to use a slash command.)
- Select the default channel that receives the answers that the outgoing webhook will send
- Choose if you want to lock the incoming webhook to the channel or that it is allowed to send to other channels as well
Choose if the trigger word has to be an exact match. - Give the URL's where the POST-request will be sent to Jump to this if you are planning to send to internal IP-addresses!
We will be using HTTPS and if you have a selfsigned certificate, you need to enable insecure connections. Here is how you do that. - Give the username that will be displayed
- Give the URL for the profile picture that will be displayed
- Click the save button
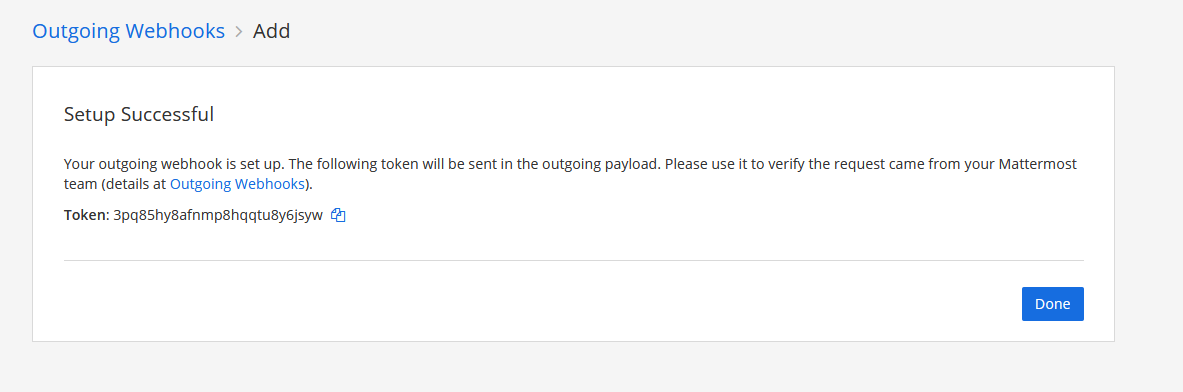
You 'll get the confirmation that the webhook is created. You get a very important token that we will be needing in our next step.
2 Write some code
Ok, you made an outgoing webhook! Now we'll write some code that can listen to your requests.
First things first, we will send encrypted https requests. It's a good habit.
1 Let's make a selfsigned certificate!
openssl req -nodes -new -x509 -keyout server.key -out server.cert
cat server.key server.cert > server.pem
Now the magical Python code (beneath is a NodeJS example)
#!/usr/bin/python3
import bottle
from bottle import Bottle, post, run, ServerAdapter,response
###CHANGE THE FOLLOWING LINES TO YOUR CONFIGURATION###
serverport = 4443
token="yourbrandnewtoken"
certfile="/path/to/your/fresh/created/server.pem"
@post("/temperature")
def hello():
response.set_header('MATTERMOST_TOKEN', token)
response.content_type = 'application/json'
return '{"text":"All is going well, thank you for your kind interest."}'
###COMMENT THIS CLASS IF YOU DON'T WANT HTTPS###
class SSLWSGIRefServer(ServerAdapter):
def run(self, handler):
from wsgiref.simple_server import make_server, WSGIRequestHandler
import ssl
if self.quiet:
class QuietHandler(WSGIRequestHandler):
def log_request(*args, **kw): pass
self.options['handler_class'] = QuietHandler
srv = make_server(self.host, self.port, handler, **self.options)
srv.socket = ssl.wrap_socket (
srv.socket,
certfile=certfile,
server_side=True)
srv.serve_forever()
if __name__ == "__main__":
'''UNCOMMENT IF YOU WANT TO RUN THE SCRIPT IN THE BACKGROUND###
try:
# Store the Fork PID
pid = os.fork()
if pid > 0:
print ('PID: %d' % pid)
os._exit(0)
except :
print ('Unable to fork. Error: ')
os._exit(1)
'''
srv = SSLWSGIRefServer(host="0.0.0.0", port=serverport)
run(server=srv)
Important note: your response has to be JSON-formatted
const https = require('https');
const fs = require('fs');
//MODIFY THE NEXT 4 LINES
const token="yourbrandnewtoken";
const keyfile="/path/to/your/just/created/server.key";
const certfile="/path/to/your/just/created/server.cert";
const serverport=4443;
const options = {
key: fs.readFileSync(keyfile),
cert: fs.readFileSync(certfile)
};
https.createServer(options, (req, res) => {
res.writeHead(200, {'Content-Type': 'application/json'});
res.writeHead(200, {'MATTERMOST_TOKEN': token});
res.write('{"text":"All is going very well, thank you for your kind interest."}');
res.end();
}).listen(serverport);
Important note: your response has to be JSON-formatted
3 More options
There are some options you can send with your response. Your response isn't limited to just text.
Commenting the post instead of answering with a new post
When you add a 'response_type' field to your response. There are three possible options "comment" or "post" or just blank "". "comment" is a reply to the message that triggered the outgoing webhook. "post" or "" create a new post.
{"text":"All is going very well, thank you for your kind interest.","post":"comment"}
Changing the username
If you want to use another username appearing as sender, you can add the username variable. This setting is default disabled and must be enabled in the Managment Console!
{"text":"All is going very well, thank you for your kind interest.","username":"The Coolest Fridge"}
Changing the profile picture
If you want to change the profile picture, add the icon_url in the request.
'{"icon_url":"https://emojipedia-us.s3.dualstack.us-west-1.amazonaws.com/thumbs/120/apple/198/freezing-face_1f976.png","text": "The Fonz says the fridge is cool enough"}'
Adding emoticons
If you want to add an emoticon in the text, add the shortcode like :tada: in the text.
'{"text": "Wow, this works :tada:"}'
Adding more lay-out
If you are not familiar with Markdown layout you can find an introduction in the Mattermost Documentation
'{"text": "| Left-Aligned | Center Aligned | Right Aligned |
| :------------ |:---------------:| -----:|
| Left column 1 | this text | $100 |
| Left column 2 | is | $10 |
| Left column 3 | centered | $1 |"}'
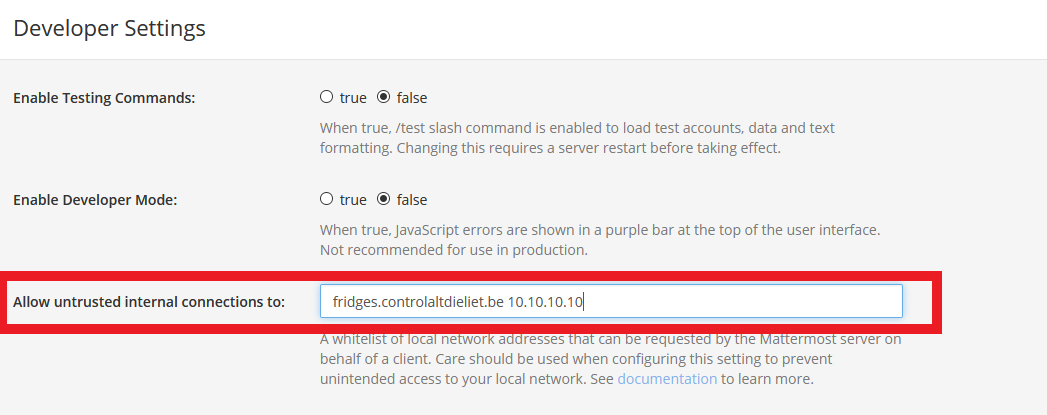
4 Allow untrusted internal connections
If you want to send your requests to your internal network, you have to specify to which hosts you want to send. Mattermost can only send to the specified internal hosts or hostnames! System Console -> Enviroment -> Developer
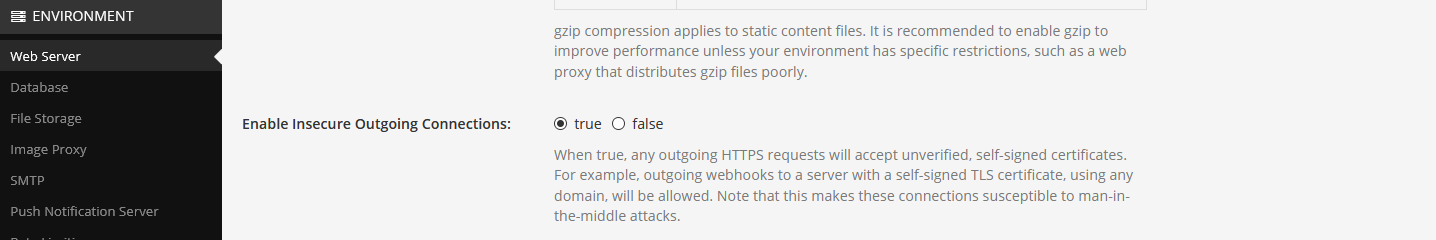
5 Unsecure outgoing connections
If you are using selsigned certificates like in our example you need to allow outgoing https connections with self-signed unverified certifcates. You find this setting in the System Console -> Enviroment -> Web Server
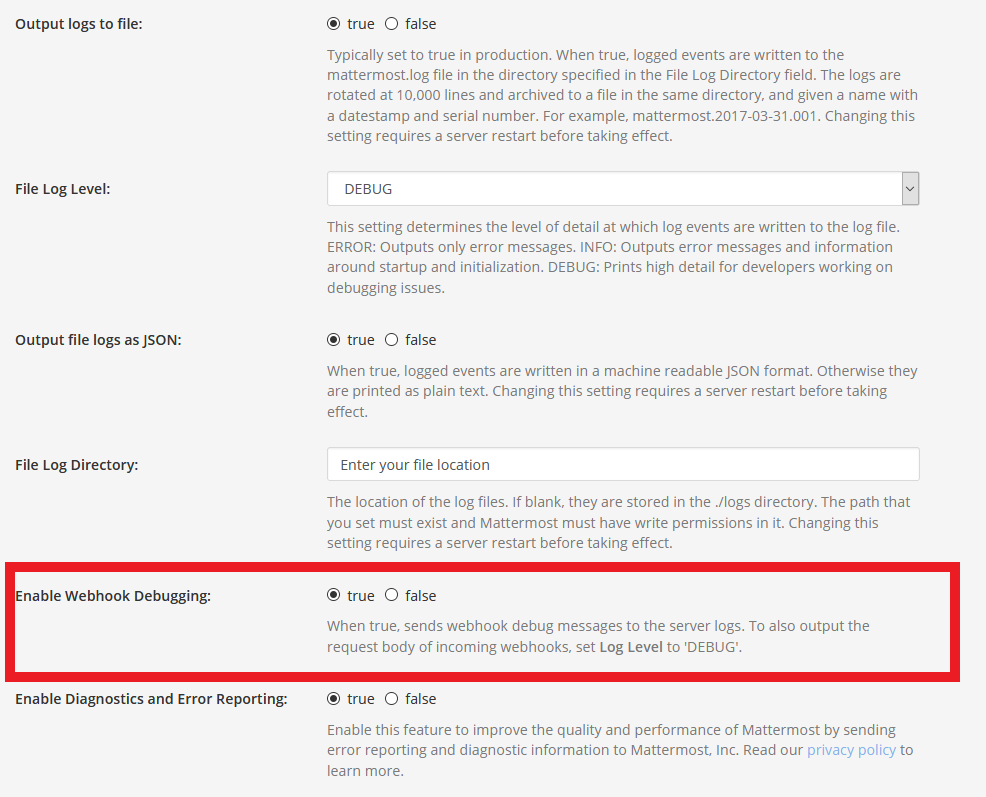
6 Debugging
Is something not working as expected? Go to the System Console and under Enviroment you find the Logging section.
In the Logging section enable Webhook Debugging and set Log Level to Debug.
You'll find in the logfiles (or in the console if you enabled logging to the console) all the relevant information.
My most common mistake is a typo in the request. It gives me an "Unable to parse incoming data" error.
7 More info
Much more info in a comprehensive way you can find in the official Mattermost Developer Documentation on Outgoing Webhooks.
You can always ask for help at the Mattermost Forum